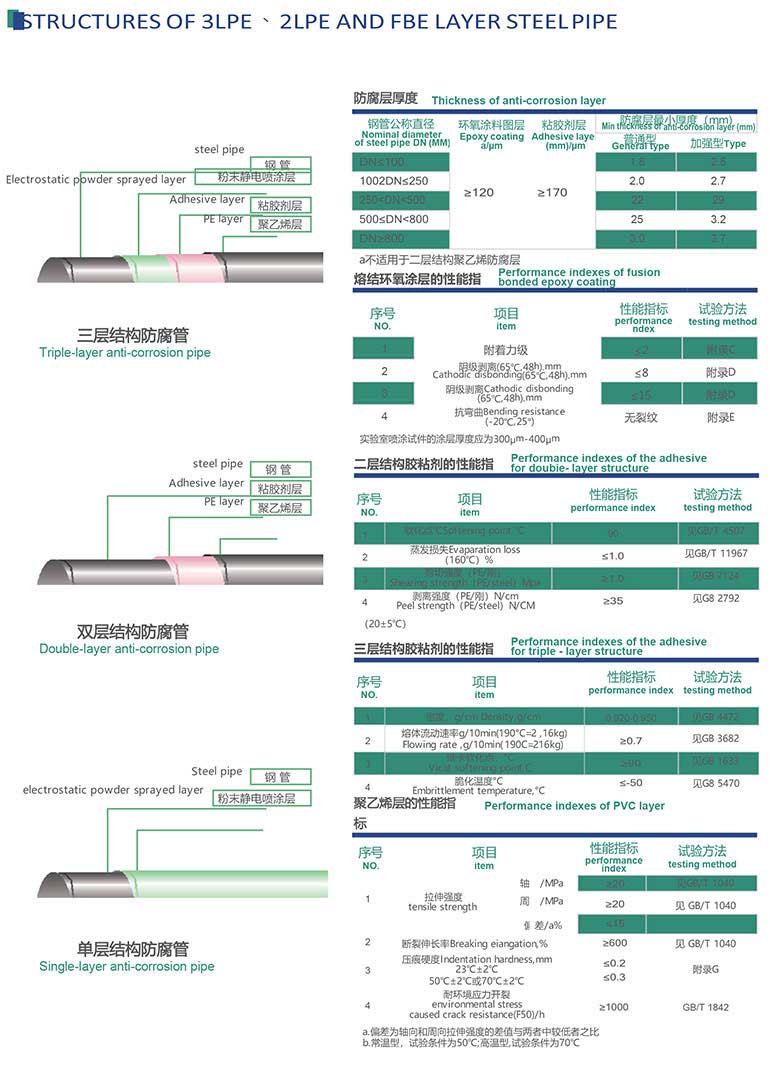
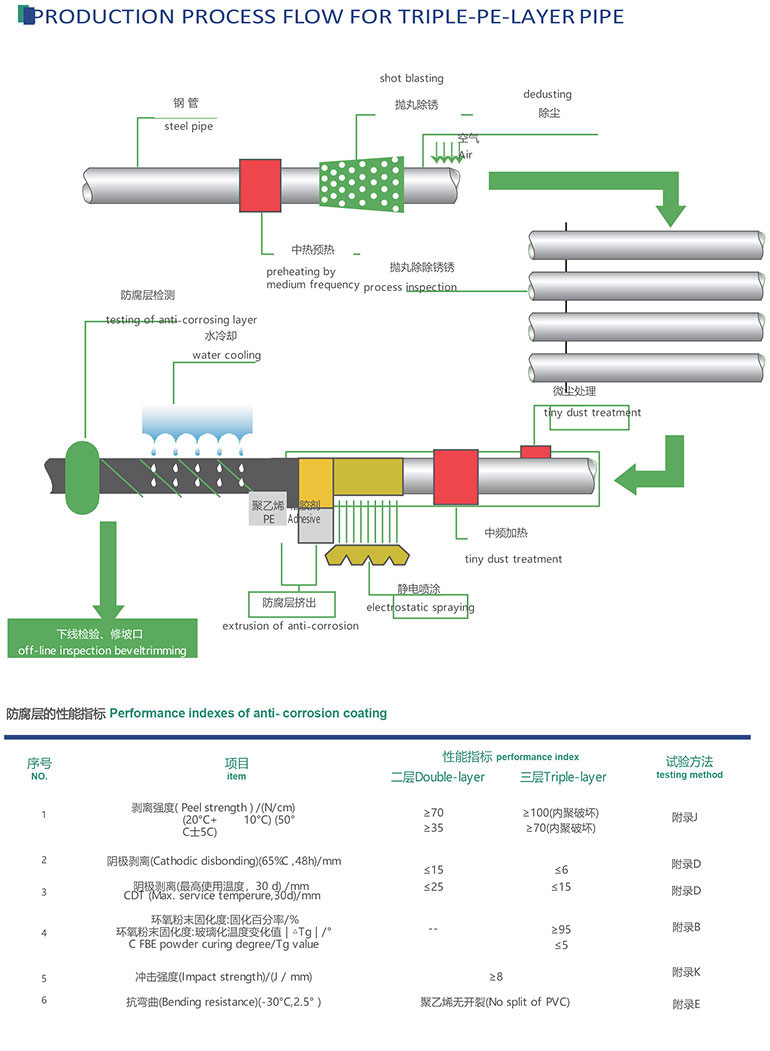
The material we used for the epoxy painting, which named thermoset power coating.
|
Raw material
|
Dosage (%)
|
|
Epoxy resin
|
30-40
|
|
Polyester resin
|
30-35
|
|
Solidified agent
|
10
|
|
colorant
|
10-15g/kg
|
The main composition of the thermoset power coating is epoxy resin (30-40%)and polyester resin (30-35%).
The following are the information connect with the epoxy resin
The most common epoxy resins are glycidyl ethers of alcohols or phenolics. Liquid epoxy resin is the diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA) and represents greater than 75% of the resin used in industrial applications.
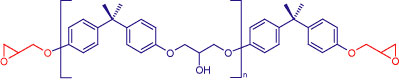
Figure 1: Structure of DGEBA resin
This resin has the consistency of honey. The epoxide group on the end of these molecules serves as the reactive site for crosslinking in these thermoset polymers. The chemical chosen to react with these epoxides is referred to as the curing agent, and it typically has active hydrogen attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. Amine curing agents are the most common and can be primary or secondary, aliphatic or aromatic, or cycloaliphatic. The amines typically have greater than three reactive sites per molecule that facilitate the formation of a three-dimensional polymer network when mixed with the epoxy resin (figure 2).
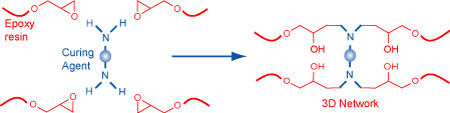
Figure 2: Curing mechanism of Epoxy resins
While the reaction of amines and epoxides occurs at room temperature and below, care must be taken in the selection of the curing agent to insure that a complete reaction takes place. Amines designed for room temperature applications typically employ plasticizers to insure complete reaction. Amines designed for heat-cured reactions use little or no plasticizers and typically give thermosets with higher strength and thermal performance.
Formulating tips for curing of epoxy resins
composite is a material reinforced by fibers or other materials with a discern-able aspect ratio of length to thickness. The fibers are primarily glass or carbon but aramid, boron and other organic and natural fibers are also used. Polymers used in composites are typically thermosets, and their purpose is to transfer the load or stresses to the fiber reinforcement in order to take advantage of the strength and stiffness (modulus) of the fibers. Typical fiber volume in this application is approximately 70%.
Applications for composites cover a broad spectrum from do-it-yourself patching and hobby kits cured at room temperature to advanced military and aerospace components cured at high temperatures. Performance and processing requirements are as diverse as the applications, so a "systems" approach must be taken when selecting the resin and curing agent for the specific application. The final physical, thermal, electrical and chemical resistance properties of the composite are determined by the choice of resin and curing agent, and the cure conditions.